How to build a Video Player in WebCodecs
In the Video Decoder section, we showed how to to build a video decoding loop in WebCodecs.
Decode Loop Demo
In the WebAudio section, we showed how to build an audio player with WebAudio.
Web Audio Player
In this guide, we’ll go over how to put these two components together to create a working video player in WebCodecs.
I don’t expect anyone to actually use this demo video player as-is in their projects. If you are working with WebCodecs, you presumably have some custom requirements that you can’t accomplish with the <video> tag.
Instead, the goal is to explain all the components you’ll need, and how to integrate them together into a working video player based on best practices.
The architecture is derived from my battle-tested production apps [1][2]. It’s not the only way to build a WebCodecs based video player, but there aren’t other good guides on how to do this, and LLMs are phenomenally bad at WebCodecs.
So consider this a starting point for building a player, and as you get more comfortable with WebCodecs, you can adjust as needed for your own use cases.
The full source code is available here.
Webcodecs Player Architecture
Section titled “Webcodecs Player Architecture”Given we’ve already covered how to play audio and to render video, the main task is to now synchronize audio and video playback.
Synchronizing Audio and Video
Section titled “Synchronizing Audio and Video”Audio as ground truth
Section titled “Audio as ground truth”We need a ground source of truth, and we’re going to choose the audio timeline as our ground source of truth. Specifically, the audio player has a AudioContext whose currentTime property is the reference point used to construct our audio timeline, as we covered in the (audio player).
We just focus on making sure the audio timeline is consistent, and we’ll know exactly where in playback we are.
Even if there is no audio track, the AudioContext will still have a currentTime property, and the audio renderer can still create a consistent timeline.
Video as a receiver
Section titled “Video as a receiver”We’re then going to construct the video renderer to render video at a given timestamp via a render function render(time).
function render(time: number){ //try to render the closest VideoFrame to time}The key word here is ‘try’. If you remember from the decoding loop, we have a render buffer of VideoFrame objects which have been decoded.
We cannot guarantee that there is a VideoFrame corresponding to the requested timestamp, or even that there is a VideoFrame that is close to the requested timestamp.
The approach is to try to find the latest VideoFrame that is before the current requested time, and render that. It is almost guaranteed that some render calls won’t be able to find a suitable VideoFrame and that’s okay, it’s normal, it’s expected.
In practice, you’ll end up skipping some frames (if playback is faster than the video framerate), or dropping some frames (if the decoder can’t keep up with playback), but this architecture will keep the video synchronized to the audio.
While the audio renderer has its own consistent timeline, we still need to regularly poll the current time from the audio renderer, and regularly make render calls to the video renderer.
For this, we’re going to create a Clock interface, for which we’ll create a regular poll mechanism called tick
function tick(){ // Poll current time from audio renderer // run render(time) // Update ui // whatever else requestAnimationFrame(tick)}In the actual player code, we’ll have an event broadcast/listener system so that we do
function tick(){ //Calculate currentTime this.emit('tick', currentTime) requestAnimationFrame(tick)}and everything else can subscribe to events
clock.on('tick', function(time: number){ /** Do whatever */})Render Loop
Section titled “Render Loop”Putting them together, we have a Clock object which regularly polls the current time from the audio render, and calls the render() function of the video renderer on every call of tick.
This will be the core of our render loop, to play both audio and video back in sync.
Loading File Data
Section titled “Loading File Data”For the audio renderer and video renderer to work, we actually need to feed them encoded audio and video data (each render handles its own decoding).
In the previous hello world examples, we just loaded the entire video’s worth of EncodedAudioChunk and EncodedVideoChunk data, which is fine for very small demo videos. If we want to handle large videos though, we’ll need to progressively load data from our source file.
Demuxer
Section titled “Demuxer”What we can do is to create a standalone file reader / demuxer, which we instantiate with a File handle, and from which we can extract track data and audio/video track segments.
Worker setup
Section titled “Worker setup”We’ll set up this demuxer in its own worker thread to isolate it from other processes. We’ll then give this worker to both the audio renderer and video renderer, so, they can fetch encoded chunks from the demuxer.
Each renderer will manage its own data lifecycle independently, independently fetching chunks from the worker, decoding and buffering data as needed, so we can keep the architecture clean and isolate concerns.
With this, the render loop should be able to indefinitely fetch and render audio and video in a synchronized fashion indefinitely.
Player object
Section titled “Player object”Now that we have our core render loop and data fetching, we need to handle for primary player events such as play, pause and seek.
To manage all of this, we’ll have a master Player interface, which will:
- Instantiate the
Demuxer,Clock,AudioRendererandVideoRenderer - Call setup functions for each
- Extract track data from the
Demuxer - Expose
play(),pause()andseek()events
Utilities
Section titled “Utilities”This is more just my personal architecture style, but we’re going to use an event based architecture, so that components can ‘listen’ for events like pause/play/seek, via an EventEmitter class we will create.
We’ll also a utility WorkerController class that lets us treat calls to workers (like the Demuxer) as async calls (e.g. await demuxer.getTrackSegment('video', start, end))
Pulling it all together
Section titled “Pulling it all together”Putting all of these together, we now have our basic, barebones architecture for our WebCodecs video player.
Play / pause / seek events will go to our clock, which will in turn propagate events to the AudioRenderer.
The player also exposes utilities for fetching the current playback time, and video metadata (such as duration), which should be everything we need to actually build a functional WebCodecs player and build a UI interface for it.
WebCodecs Player Components
Section titled “WebCodecs Player Components”Now that we have the high level architecture, we’ll actually include the code components for each.
File Loader
Section titled “File Loader”First, we’ll create our Demuxer. There are multiple libraries for demuxing like Mediabunny and web-demuxer but I’ll use my own demuxer since that’s what I use in production.
You can see how to build a Mediabunny based player here
The demuxing library already has all the methods, so we’re just creating a worker wrapper around the main methods.
Demuxer
import { MP4Demuxer } from 'webcodecs-utils';
/** * File Worker - Pure MP4 Demuxer * * Responsibilities: * - Load and parse MP4 files * - Extract track metadata * - Extract video/audio chunks for specific time ranges * - Send chunks to video worker via MessagePort * - Send chunks to audio player via direct worker messages */
let demuxer: MP4Demuxer | null = null;let videoWorkerPort: MessagePort | null = null;
// Worker message handlerself.onmessage = async function(event: MessageEvent) { const { cmd, data, request_id } = event.data;
try { switch (cmd) { case 'init': // Initialize demuxer with file const { file, videoPort } = data; demuxer = new MP4Demuxer(file); await demuxer.load();
// Store the MessagePort for video worker communication if (videoPort) { videoWorkerPort = videoPort; videoWorkerPort.onmessage = handleVideoWorkerMessage; }
self.postMessage({ request_id, res: true }); break;
case 'get-tracks': if (!demuxer) { throw new Error('Demuxer not initialized'); }
const tracks = demuxer.getTracks();
self.postMessage({ request_id, res: tracks }); break;
case 'get-audio-segment': if (!demuxer) { throw new Error('Demuxer not initialized'); }
const { start, end } = data; const audioChunks = await demuxer.extractSegment('audio', start, end);
// Send directly back to audio player (main thread) self.postMessage({ request_id, res: audioChunks }); break;
case 'get-video-segment': // This is called from main thread, but we forward to video worker if (!demuxer || !videoWorkerPort) { throw new Error('Demuxer or video port not initialized'); }
const videoSegment = await demuxer.extractSegment( 'video', data.start, data.end );
// Send chunks to video worker via MessagePort videoWorkerPort.postMessage({ cmd: 'chunks', request_id, res: videoSegment }); break;
default: throw new Error(`Unknown command: ${cmd}`); } } catch (error) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: error instanceof Error ? error.message : String(error) }); }};
// Handle messages from video worker (via MessagePort)function handleVideoWorkerMessage(event: MessageEvent) { const { cmd, data, request_id } = event.data;
if (!demuxer || !videoWorkerPort) return;
switch (cmd) { case 'request-segment': // Video worker requests a segment demuxer.extractSegment('video', data.start, data.end) .then(chunks => { videoWorkerPort!.postMessage({ cmd: 'chunks', request_id, res: chunks }); }) .catch(error => { videoWorkerPort!.postMessage({ cmd: 'error', request_id, error: error instanceof Error ? error.message : String(error) }); }); break; }}Audio Renderer
Section titled “Audio Renderer”For the audio renderer, we’re going to make two more changes compared to the WebAudio tutorial, which is to not load the entire video’s audio in into memory via decodeAudioData(await file.arrayBuffer()).
WebCodecs <> WebAudio
Section titled “WebCodecs <> WebAudio”Our WebAudio demos just loaded mp3 demos (the file in file.arrayBuffer() was an mp3 file), but here we now need to handle video file inputs. Our Demuxer library can extract audio data from a video file, but it returns data as EncodedAudioChunk[].
Rather than decoding the audio data into AudioData[], extracting Float32Array channel data, constructing AudioBuffers and copying channel data over, it’s a lot faster and compute efficient to just mux our EncodedAudioChunk[] into a virtual file
import { Muxer, ArrayBufferTarget } from 'mp4-muxer'muxEncodedChunksToBuffer(chunks: EncodedAudioChunk[], config: AudioTrackData): ArrayBuffer { // Create MP4 muxer const muxer = new Muxer({ target: new ArrayBufferTarget(), fastStart: 'in-memory', firstTimestampBehavior: 'offset', audio: { codec: 'aac', sampleRate: config.sampleRate, numberOfChannels: config.numberOfChannels } }); for (const chunk of chunks) { muxer.addAudioChunk(chunk); }
await muxer.finalize(); return muxer.target.buffer;}We can then load the AudioBuffer using ctx.decodeAudioData. It feels hacky, but it’s faster and more efficient.
const muxedBuffer = this.muxEncodedChunksToBuffer(<EncodedAudioChunk> chunks, this.audioConfig!);const audioBuffer = <AudioBuffer> await this.audioContext!.decodeAudioData(muxedBuffer);Segmented Loading
Section titled “Segmented Loading”The other change we’ll make is to load the audio is ‘segments’ of 30 seconds, to avoid loading potentially hours worth of raw audio into memory and causing memory issues.
async loadSegment(time: number) { const segmentIndex = Math.floor(time / SEGMENT_DURATION); // Check cache first if (this.audioSegments.has(segmentIndex)) { return this.audioSegments.get(segmentIndex); } // Fetch EncodedAudioChunks for this segment const encodedChunks = await this.getEncodedChunksForTime(segmentIndex * SEGMENT_DURATION); try { const muxedBuffer = await this.muxEncodedChunksToBuffer(encodedChunks, this.audioConfig!); const audioBuffer = await this.audioContext!.decodeAudioData(muxedBuffer); this.audioSegments.set(segmentIndex, audioBuffer); // Cache for later return audioBuffer; } catch (error) { console.error('Error loading audio segment:', error); return null; }}We’ll store these buffers in a cache, and can pre-load them and clean them up as needed.
async preloadNextSegment(startTime: number) { if (this.isPreloading || startTime >= this.duration) return;
const nextSegmentIndex = Math.floor(startTime / SEGMENT_DURATION); // Check if we already have this segment cached if (this.audioSegments.has(nextSegmentIndex)) return; this.isPreloading = true;
try { const nextSegment = await this.loadSegment(startTime); if (!nextSegment || !this.isPlaying) return; this.scheduleSegment(nextSegment, startTime, 0); } finally { this.isPreloading = false; }}And we schedule future segments for playback
scheduleSegment(audioBuffer: AudioBuffer, startTime: number, offset: number) { const sourceNode = this.audioContext!.createBufferSource(); sourceNode.buffer = audioBuffer; sourceNode.connect(this.audioContext!.destination);
const playbackTime = this.startTime + (startTime - this.pauseTime);
sourceNode.start(playbackTime, offset); // Clean up completed nodes sourceNode.onended = () => { sourceNode.disconnect(); this.scheduledNodes.delete(startTime); };}Complete Audio Renderer
Section titled “Complete Audio Renderer”This gives us a complete audio renderer with segmented loading
Full Audio Renderer
import {ArrayBufferTarget, Muxer} from "mp4-muxer";import EventEmitter from "../../../utils/EventEmitter";import { WorkerController } from "../../../utils/WorkerController";import { VideoWorker } from "../video/video";export interface AudioTrackData { codec: string, sampleRate: number , numberOfChannels: number}
// Duration of each audio segment (time-based blocks that contain multiple EncodedAudioChunks)const SEGMENT_DURATION = 30; // seconds
export interface AudioPlayerArgs { audioConfig: AudioTrackData; duration: number; worker: WorkerController; file: File;}
export class WebAudioPlayer { audioContext: AudioContext | null; sourceNode: AudioBufferSourceNode | null; isPlaying: boolean; startTime: number; pauseTime: number; duration: number; encodedChunks: EncodedAudioChunk[]; // EncodedAudioChunks from current segment audioSegments: Map<number, AudioBuffer>; // Decoded audio segments (segmentIndex -> AudioBuffer) scheduledNodes: Map<number, AudioBufferSourceNode>; preloadThreshold: number; // Seconds before segment end to trigger preload file: File;
worker: WorkerController; isPreloading: boolean; audioConfig: AudioTrackData | null; constructor(args: AudioPlayerArgs) { this.audioContext = null; this.sourceNode = null; this.isPlaying = false; this.startTime = 0; this.pauseTime = 0; this.duration = args.duration; this.audioConfig = args.audioConfig; this.encodedChunks = []; this.audioSegments = new Map(); // Cache for decoded audio segments this.scheduledNodes = new Map(); // Track scheduled audio nodes this.preloadThreshold = 5; // Seconds before segment end to trigger preload this.isPreloading = false; this.worker = args.worker; this.file = args.file; this.init(); }
init() { this.audioContext = new AudioContext(); this.seek(0);
}
/** * Mux EncodedAudioChunks to an ArrayBuffer for Web Audio API decoding * @param chunks - Array of EncodedAudioChunks from a segment */ async muxEncodedChunksToBuffer(chunks: EncodedAudioChunk[], config: AudioTrackData) { // Create MP4 muxer const muxer = new Muxer({ target: new ArrayBufferTarget(), fastStart: 'in-memory', firstTimestampBehavior: 'offset', audio: { codec: 'aac', sampleRate: config.sampleRate, numberOfChannels: config.numberOfChannels } });
// Add EncodedAudioChunks to muxer for (const chunk of chunks) { muxer.addAudioChunk(chunk); }
// Finalize and get array buffer await muxer.finalize(); return muxer.target.buffer; }
/** * Fetch EncodedAudioChunks for a specific time segment from the file worker * @param time - Time in seconds * @returns Array of EncodedAudioChunks */ async getEncodedChunksForTime(time: number) { const segmentIndex = Math.floor(time / SEGMENT_DURATION);
const chunks = <EncodedAudioChunk[]> await this.worker.sendMessage('get-audio-segment', { start: segmentIndex * SEGMENT_DURATION, end: segmentIndex * SEGMENT_DURATION + SEGMENT_DURATION, file: this.file });
this.encodedChunks = chunks;
return chunks; }
/** * Load and decode an audio segment * @param time - Time in seconds * @returns Decoded AudioBuffer for the segment */ async loadSegment(time: number) { const segmentIndex = Math.floor(time / SEGMENT_DURATION);
// Check cache first if (this.audioSegments.has(segmentIndex)) { return this.audioSegments.get(segmentIndex); }
// Fetch EncodedAudioChunks for this segment const encodedChunks = await this.getEncodedChunksForTime(segmentIndex * SEGMENT_DURATION); if (encodedChunks.length === 0) return null;
try { // Mux EncodedAudioChunks to AAC buffer const muxedBuffer = await this.muxEncodedChunksToBuffer(encodedChunks, this.audioConfig!); // Decode to AudioBuffer for Web Audio API const audioBuffer = await this.audioContext!.decodeAudioData(muxedBuffer); // Cache the decoded segment this.audioSegments.set(segmentIndex, audioBuffer);
return audioBuffer; } catch (error) { console.error('Error loading audio segment:', error); return null; } }
async startPlayback(startFrom = this.pauseTime) { // Clear any previously scheduled nodes this.clearScheduledNodes();
const currentSegment = await this.loadSegment(startFrom);
if (!currentSegment) return;
const segmentOffset = startFrom % SEGMENT_DURATION; const timeUntilEnd = SEGMENT_DURATION - segmentOffset;
// Schedule current segment this.scheduleSegment(currentSegment, startFrom, segmentOffset);
// Pre-load and schedule next segment this.preloadNextSegment(startFrom + timeUntilEnd); }
clearScheduledNodes() { // Clear both audio nodes and preload timeouts for (const node of this.scheduledNodes.values()) { node.stop(); node.disconnect(); } this.scheduledNodes.clear(); }
getCurrentSegmentIndex() { return Math.floor(this.getCurrentTime() / SEGMENT_DURATION); }
async preloadNextSegment(startTime: number) { if (this.isPreloading || startTime >= this.duration) return;
const nextSegmentIndex = Math.floor(startTime / SEGMENT_DURATION);
// Check if we already have this segment cached if (this.audioSegments.has(nextSegmentIndex)) { this.scheduleSegment(this.audioSegments.get(nextSegmentIndex), startTime, 0); return; } this.isPreloading = true; try { const nextSegment = await this.loadSegment(startTime); if (!nextSegment || !this.isPlaying) return;
this.scheduleSegment(nextSegment, startTime, 0);
// Instead of setTimeout, we'll check during playback updates } finally { this.isPreloading = false; } }
scheduleSegment(audioBuffer: AudioBuffer, startTime: number, offset: number) { const sourceNode = this.audioContext!.createBufferSource(); sourceNode.buffer = audioBuffer; sourceNode.connect(this.audioContext!.destination); const playbackTime = this.startTime + (startTime - this.pauseTime); sourceNode.start(playbackTime, offset); this.scheduledNodes.set(startTime, sourceNode);
// Clean up completed nodes sourceNode.onended = () => { sourceNode.disconnect(); this.scheduledNodes.delete(startTime); }; }
async play() { this.startTime = this.audioContext!.currentTime; await this.startPlayback(); this.isPlaying = true; }
async pause() { this.clearScheduledNodes(); this.pauseTime = this.getCurrentTime(); this.isPlaying = false; }
async seek(time: number) { const wasPlaying = this.isPlaying; if (wasPlaying) { this.clearScheduledNodes(); this.isPlaying = false; } this.pauseTime = time; if (wasPlaying) { this.startTime = this.audioContext!.currentTime; this.isPlaying = true; await this.startPlayback(time);
} }
checkForPreLoad() { if (!this.isPlaying) return; const currentTime = this.getCurrentTime(); // Check if we need to preload the next segment const currentSegmentIndex = this.getCurrentSegmentIndex(); const timeInCurrentSegment = currentTime % SEGMENT_DURATION;
if (timeInCurrentSegment >= (SEGMENT_DURATION - this.preloadThreshold) && !this.isPreloading && !this.audioSegments.has(currentSegmentIndex + 1)) { this.preloadNextSegment((currentSegmentIndex + 1) * SEGMENT_DURATION); } }
getCurrentTime() { if (!this.isPlaying) return this.pauseTime; return this.pauseTime + (this.audioContext!.currentTime - this.startTime); }}VideoRenderer
Section titled “VideoRenderer”For the video renderer, we will create a VideoRenderer class using the same decode patterns covered in the decoding loop section.
VideoRenderer
import { GPUFrameRenderer } from 'webcodecs-utils';
export interface VideoTrackData { codec: string, codedHeight: number, codedWidth: number, description: Uint8Array, frameRate: number }
export default class VideoRenderer {
lastRenderedTime: number = 0; currentChunk: number = 0; firstRendered: boolean = false; source_buffer: EncodedVideoChunk[] = []; rendered_buffer: VideoFrame[] = []; canvas: OffscreenCanvas; frameRenderer: GPUFrameRenderer; decoder: VideoDecoder; metadata: VideoTrackData; initP: Promise<void> constructor(metadata: VideoTrackData, chunks: EncodedVideoChunk[], canvas: OffscreenCanvas, frameRenderer: GPUFrameRenderer) {
console.log(chunks[0])
this.currentChunk =0; this.firstRendered = false;
this.source_buffer = chunks; this.rendered_buffer = [];
this.metadata = metadata;
this.frameRenderer = frameRenderer;
this.canvas = canvas;
// Initialize GPU renderer with linear filtering (hardware accelerated)
this.initP = this.frameRenderer.init();
this.decoder = this.setupDecoder(metadata)
this.lastRenderedTime = 0;
this.fillBuffer(); }
setupDecoder(metadata: VideoTrackData){
const decoder = new VideoDecoder({ output: function (this: VideoRenderer, frame: VideoFrame){
if(!this.firstRendered) { this.firstRendered = true;
this.renderFrame(frame) } else {
if(frame.timestamp/1e6 < this.lastRenderedTime) { frame.close(); if(this.rendered_buffer.length < 10) { this.fillBuffer(); } return; } this.rendered_buffer.push(frame) }
}.bind(this),
error: function (this: VideoRenderer, error: Error){ console.warn(error); }.bind(this) },
)
decoder.configure(metadata);
return decoder;
}
play(){
} async seek(time: number){
for(let i=0; i < this.rendered_buffer.length; i++){ this.rendered_buffer[i].close() } this.rendered_buffer = [];
let lastKeyFrame = 0;
for(let i=0; i< this.source_buffer.length; i++){ if(this.source_buffer[i].type === "key" && this.source_buffer[i].timestamp < time*1e6) lastKeyFrame = i }
let renderTill =lastKeyFrame; for(let i=lastKeyFrame; i< this.source_buffer.length; i++){ if(this.source_buffer[i].timestamp < time*1e6) renderTill = i }
for (let i=lastKeyFrame; i< renderTill; i++){ this.decoder.decode(this.source_buffer[i]); }
this.currentChunk = renderTill;
}
getLatestFrame(time: number){
for (let i=0; i < this.rendered_buffer.length-1; i++){
if(this.rendered_buffer[i+1].timestamp < this.rendered_buffer[i].timestamp){ return i+1; } }
if(this.rendered_buffer[0].timestamp/1e6 > time) return -1;
let latest_frame_buffer_index = 0;
for (let i=0; i < this.rendered_buffer.length; i++){
if (this.rendered_buffer[i].timestamp/1000 < time && this.rendered_buffer[i].timestamp > this.rendered_buffer[latest_frame_buffer_index].timestamp){ latest_frame_buffer_index = i } }
return latest_frame_buffer_index;
} render(time: number){
this.lastRenderedTime = time;
if(this.rendered_buffer.length > 0){
const latest_frame = this.getLatestFrame(time);
if(latest_frame > -1){
for(let i=0; i < latest_frame-1; i++){ this.rendered_buffer[i].close() } this.rendered_buffer.splice(0, latest_frame-1); //Drop frames
const frame_to_render = this.rendered_buffer.shift();
this.renderFrame(frame_to_render); if(this.rendered_buffer.length < 5) this.fillBuffer(); }
}
}
fillBuffer(){
for(let i=0; i < 10; i++){ if(this.currentChunk +i < this.source_buffer.length){ try{
if (this.decoder.state !== 'configured') {
console.log("resetting decoder")
this.decoder = this.setupDecoder(this.metadata);
for(let j=this.currentChunk; j < this.source_buffer.length; j++){ if(this.source_buffer[j].type === "key"){ this.currentChunk = j; break; } } } this.decoder.decode(this.source_buffer[this.currentChunk]); this.currentChunk +=1 } catch (e) { console.log(e); } } }
}
async renderFrame(frame: VideoFrame){
await this.initP;
try{
if(frame.timestamp < this.lastRenderedTime) { frame.close(); return; }
// Use GPU renderer for zero-copy rendering this.frameRenderer.drawImage(frame); frame.close();
} catch (e) { console.log(e); }
}
}However, just like in the audio renderer, we’ll enable chunked loading so that we can load encoded video segments in chunks. We’ll store this in a VideoWorker, since this will also be loaded inside of a worker. The VidoeWorker will manage multiple VideoRenderers, and will dynamically load each and redirect render calls appropriately.
Video Worker
import VideoRenderer, { VideoTrackData } from "./decoder";import { GPUFrameRenderer } from 'webcodecs-utils';
// Typesinterface TrackData { duration: number; audio?: AudioTrackData; video?: VideoTrackData;}
interface AudioTrackData { codec: string; sampleRate: number; numberOfChannels: number;}
// Connection to file workerlet fileWorkerPort: MessagePort | null = null;
// Active video transformerlet videoManager: VideoTransformer | null = null;
// The canvas we'll render tolet offscreenCanvas: OffscreenCanvas | null = null;
// Same chunk duration as used in audioconst CHUNK_DURATION = 300; // Duration of each chunk in seconds
/** * ChunkedVideoManager manages multiple VideoRenderer instances, one per chunk * Each VideoRenderer is responsible for rendering frames from its own chunk */export default class VideoTransformer { private videoMetadata: VideoTrackData | undefined; private duration: number | undefined; private canvas: OffscreenCanvas; private filePort: MessagePort;
// Map of chunk index to VideoRenderer private renderers: Map<number, VideoRenderer>; // Cached chunks data private loadedChunks: Map<number, EncodedVideoChunk[]>;
// Current state private currentChunkIndex: number; private activeRenderer: VideoRenderer | null; private isPreloading: boolean; private preloadThreshold: number; private rendering: boolean; private frameRenderer: GPUFrameRenderer; private lastRenderedTime: number;
// Request ID tracking private requestId: number = 0; private pendingRequests: Map<number, { resolve: (value: any) => void, reject: (error: any) => void }> = new Map();
constructor( canvas: OffscreenCanvas, filePort: MessagePort, videoMetadata: VideoTrackData, duration: number ) { this.canvas = canvas; this.filePort = filePort; this.videoMetadata = videoMetadata; this.frameRenderer = new GPUFrameRenderer(this.canvas, { filterMode: 'linear' }); this.duration = duration; this.renderers = new Map(); this.loadedChunks = new Map(); this.currentChunkIndex = -1; this.activeRenderer = null; this.isPreloading = false; this.preloadThreshold = 5; // Seconds before chunk end to trigger preload this.rendering = false; this.lastRenderedTime = 0;
// Set up message handler for file worker responses this.filePort.onmessage = this.handleFileWorkerMessage.bind(this); }
private handleFileWorkerMessage(event: MessageEvent) { const { cmd, request_id, res, error } = event.data;
if (cmd === 'chunks' && request_id) { const pending = this.pendingRequests.get(request_id); if (pending) { if (error) { pending.reject(new Error(error)); } else { pending.resolve(res); } this.pendingRequests.delete(request_id); } } }
private requestSegment(start: number, end: number): Promise<EncodedVideoChunk[]> { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { const id = ++this.requestId; this.pendingRequests.set(id, { resolve, reject });
this.filePort.postMessage({ cmd: 'request-segment', request_id: id, data: { start, end } }); }); }
async initialize(){ // Initialize with the first chunk await this.initializeChunk(0); await this.seek(0); await this.frameRenderer.init(); }
/** * Get the chunk index for a specific time */ private getChunkIndexForTime(time: number): number { return Math.floor(time / CHUNK_DURATION); }
/** * Load a specific chunk from the file worker */ private async loadChunk(chunkIndex: number): Promise<EncodedVideoChunk[]> { // If already loaded, return from cache if (this.loadedChunks.has(chunkIndex)) { return this.loadedChunks.get(chunkIndex) || []; }
const startTime = chunkIndex * CHUNK_DURATION; const endTime = Math.min((chunkIndex + 1) * CHUNK_DURATION, this.duration);
try { // Request chunks from file worker via MessagePort const chunks = await this.requestSegment(startTime, endTime);
// Cache the chunks this.loadedChunks.set(chunkIndex, chunks);
return chunks; } catch (error) { console.error('Error loading video chunk:', error); return []; } }
/** * Initialize a renderer for a specific chunk */ private async initializeChunk(chunkIndex: number): Promise<VideoRenderer | null> { // If we already have a renderer for this chunk, return it if (this.renderers.has(chunkIndex)) { return this.renderers.get(chunkIndex) || null; }
// Load chunks for this time segment const chunks = await this.loadChunk(chunkIndex); if (chunks.length === 0) { console.error(`No chunks loaded for index ${chunkIndex}`); return null; }
// Create a new renderer with these chunks const renderer = new VideoRenderer( this.videoMetadata, chunks, this.canvas, this.frameRenderer );
// Store it in our map this.renderers.set(chunkIndex, renderer);
// Start preloading the next chunk this.preloadNextChunk(chunkIndex + 1);
return renderer; }
/** * Preload the next chunk in background */ private async preloadNextChunk(chunkIndex: number) { if (this.isPreloading || chunkIndex * CHUNK_DURATION >= this.duration || this.loadedChunks.has(chunkIndex)) { return; }
this.isPreloading = true; try { await this.loadChunk(chunkIndex); } finally { this.isPreloading = false; } }
/** * Check if we need to preload the next chunk based on current time */ private checkPreloadNextChunk(currentTime: number) { const currentChunkIndex = this.getChunkIndexForTime(currentTime); const timeInCurrentChunk = currentTime % CHUNK_DURATION;
if (timeInCurrentChunk >= (CHUNK_DURATION - this.preloadThreshold) && !this.isPreloading && !this.loadedChunks.has(currentChunkIndex + 1)) { this.preloadNextChunk(currentChunkIndex + 1); }
// Also, if we're close to the end of the chunk, initialize the next renderer if (timeInCurrentChunk >= (CHUNK_DURATION - this.preloadThreshold) && !this.renderers.has(currentChunkIndex + 1) && this.loadedChunks.has(currentChunkIndex + 1)) { this.initializeChunk(currentChunkIndex + 1); } }
/** * Get debug information about the current state */ getDebugInfo() {
return { currentChunkIndex: this.currentChunkIndex, activeRenderer: this.activeRenderer ? { renderBufferSize: this.activeRenderer.rendered_buffer.length, decodeQueueSize: this.activeRenderer.decoder.decodeQueueSize, currentChunk: this.activeRenderer.currentChunk, lastRenderedTime: this.activeRenderer.lastRenderedTime
} : null, totalRenderers: this.renderers.size, loadedChunks: this.loadedChunks.size, isPreloading: this.isPreloading }; }
/** * Play the video (compatibility with VideoRenderer API) */ play() { // No-op, just for compatibility }
/** * Render the video at the specified time */ render(time: number) {
if (this.rendering) { return; }
;
this.rendering = true; this.lastRenderedTime = time;
try { // Get the chunk index for this time const chunkIndex = this.getChunkIndexForTime(time);
// If we need to switch to a different chunk if (chunkIndex !== this.currentChunkIndex || !this.activeRenderer) { // Schedule the chunk switch asynchronously but don't await it this.switchToChunk(chunkIndex, time).then(() => { this.rendering = false; }); return; }
// Render using the active renderer if (this.activeRenderer) { this.activeRenderer.render(time); }
// Check if we need to preload this.checkPreloadNextChunk(time);
} finally { this.rendering = false; } }
/** * Switch to a different chunk renderer */ private async switchToChunk(chunkIndex: number, time: number) { console.log(`Switching to chunk ${chunkIndex} at time ${time}`);
// Initialize the chunk renderer if needed if (!this.renderers.has(chunkIndex)) { this.activeRenderer = await this.initializeChunk(chunkIndex); } else { this.activeRenderer = this.renderers.get(chunkIndex) || null; }
if (!this.activeRenderer) { console.error(`Failed to initialize renderer for chunk ${chunkIndex}`); return; }
// Update current chunk index this.currentChunkIndex = chunkIndex;
// Calculate the local time within this chunk const relativeTime = time - (chunkIndex * CHUNK_DURATION);
// Seek within the chunk await this.activeRenderer.seek(time);
// Render the frame this.activeRenderer.render(time);
// Start preloading next chunk this.preloadNextChunk(chunkIndex + 1); }
/** * Seek to a specific time position */ async seek(time: number) { const chunkIndex = this.getChunkIndexForTime(time);
// If we're already in this chunk, use the active renderer if (chunkIndex === this.currentChunkIndex && this.activeRenderer) { await this.activeRenderer.seek(time); return; }
// Otherwise, switch to the correct chunk await this.switchToChunk(chunkIndex, time); }
/** * Clean up resources */ terminate() { // Clean up all renderers for (const renderer of this.renderers.values()) { // VideoRenderer doesn't have a terminate method, // but we could add one if needed }
this.renderers.clear(); this.loadedChunks.clear(); this.activeRenderer = null; }}
let transformer: VideoTransformer | null = null;
// Main message handlerself.onmessage = async function(event: MessageEvent) { const { cmd, data, request_id } = event.data;
switch (cmd) { case "init": try { // Get the transferred canvas and file worker port offscreenCanvas = data.canvas; fileWorkerPort = data.fileWorkerPort;
if (!offscreenCanvas || !fileWorkerPort) { throw new Error('Missing canvas or file worker port'); }
console.log("Video worker initialized with MessagePort to file worker");
// Send successful initialization (video transformer will be created after track data is received) self.postMessage({ request_id, res: true }); } catch (error) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: `Initialization error: ${error}` }); } break;
case "set-track-data": try { // Receive video metadata and duration from main thread const { videoMetadata, duration } = data;
if (!offscreenCanvas || !fileWorkerPort) { throw new Error('Worker not initialized'); }
// Set canvas dimensions if (videoMetadata.codedWidth && videoMetadata.codedHeight) { offscreenCanvas.width = videoMetadata.codedWidth; offscreenCanvas.height = videoMetadata.codedHeight; }
// Create the video transformer with the file worker port transformer = new VideoTransformer( offscreenCanvas, fileWorkerPort, videoMetadata, duration );
await transformer.initialize(); console.log("Video transformer initialized");
self.postMessage({ request_id, res: true }); } catch (error) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: `Set track data error: ${error}` }); } break;
case "render": if (!transformer) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: "VideoManager not initialized" }); return; }
try { const time = data.time; transformer.render(time); self.postMessage({ request_id, res: "render-complete" }); } catch (error) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: `Render error: ${error}` }); } break;
case "get-debug-info": if (!transformer) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: "VideoManager not initialized" }); return; }
try { const debugInfo = transformer.getDebugInfo(); self.postMessage({ request_id, res: debugInfo }); } catch (error) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: `Debug info error: ${error}` }); } break;
case "seek": if (!transformer) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: "VideoManager not initialized" }); return; }
try { const time = data.time; await transformer.seek(time); self.postMessage({ request_id, res: "seek-complete" }); } catch (error) { self.postMessage({ request_id, error: `Seek error: ${error}` }); } break;
case "terminate": if (transformer) { transformer.terminate(); transformer = null; } self.postMessage({ request_id, res: "terminated" }); break; }};Finally, we’ll create a simple wrapper around the video worker, which can be called by the player on the main thread, and which will propagate events to the VideoWorker worker.
Video Wrapper
import EventEmitter from "../../../utils/EventEmitter";import workerUrl from './video.worker.ts?worker&url';import { WorkerController } from "../../../utils/WorkerController";
export interface VideoWorkerParams { src: File; canvas: HTMLCanvasElement; fileWorkerPort: MessagePort;}
/** * OffscreenVideoWorker is a wrapper around the video.worker.ts * It handles communication with the worker and provides a simple interface. */export class VideoWorker extends EventEmitter { private canvas: HTMLCanvasElement; private offscreenCanvas: OffscreenCanvas | null = null; public duration: number = 0; private worker: WorkerController; private fileWorkerPort: MessagePort;
constructor(params: VideoWorkerParams) { super(); this.canvas = params.canvas; this.fileWorkerPort = params.fileWorkerPort; this.worker = new WorkerController(workerUrl); }
/** * Send a message to the worker and wait for a response */
/** * Initialize the video player */ async initialize(): Promise<void> { // Create the offscreen canvas this.offscreenCanvas = this.canvas.transferControlToOffscreen();
// Initialize the worker with the offscreen canvas and file worker port const initialized = await this.worker.sendMessage('init', { canvas: this.offscreenCanvas, fileWorkerPort: this.fileWorkerPort }, [this.offscreenCanvas, this.fileWorkerPort]);
// Emit initialization event this.emit('initialized', initialized); }
/** * Seek to a specific time */ async seek(time: number): Promise<void> { // Send seek command to worker await this.worker.sendMessage('seek', { time }); }
/** * Get debug information from the video worker */ async getDebugInfo(): Promise<any> { return await this.worker.sendMessage('get-debug-info', {}); }
async setTrackData(videoMetadata: any, duration: number): Promise<void> { await this.worker.sendMessage('set-track-data', { videoMetadata, duration }); } /** * Clean up resources */ terminate(): void {
// Terminate the worker this.worker.sendMessage('terminate').catch(console.error);
// Clean up this.worker.terminate(); this.offscreenCanvas = null;
// Emit terminate event this.emit('terminated'); }
/**
/** * Update the current frame (animation loop) */
render(time: number): void {
// Send render command to worker this.worker.sendMessage('render', { time: time }); }}With all three of those components, we’ll be able to run render calls video.render() -> videoWorker.render() -> videoRenderer.render
Next, we have the Clock class which will manage the update loop via the tick handler, and broadcast updates to the VideoWorker and AudioRenderer.
Clock class
import EventEmitter from '../utils/EventEmitter';import { WebAudioPlayer } from './renderers/audio/audio';import { VideoWorker } from './renderers/video/video';
export class Clock extends EventEmitter {
private audioPlayer: WebAudioPlayer; private videoWorker: VideoWorker; private isPlaying: boolean = false; private animationFrame: number | null = null; private duration: number;
// Frame rate management private readonly TARGET_FPS = 30; // Target 30fps for smooth playback private readonly FRAME_INTERVAL: number; private lastFrameTime = 0;
/** * Create a new Clock * @param audioPlayer - Audio player with Web Audio timeline * @param videoWorker - Video worker for passive rendering * @param duration - Total video duration in seconds */ constructor(audioPlayer: WebAudioPlayer, videoWorker: VideoWorker, duration: number) { super();
this.audioPlayer = audioPlayer; this.videoWorker = videoWorker; this.duration = duration; this.FRAME_INTERVAL = 1000 / this.TARGET_FPS; }
/** * Start playback * * Starts the audio player and begins the tick loop. * The tick loop queries the audio timeline and drives video rendering. */ async play(): Promise<void> { if (this.isPlaying) return;
this.isPlaying = true;
// Start audio playback (this starts the timeline) await this.audioPlayer.play();
// Start the tick loop this.lastFrameTime = performance.now(); this.tick();
this.emit('play'); }
/** * Pause playback * * Pauses audio and stops the tick loop. */ pause(): void { if (!this.isPlaying) return;
this.isPlaying = false;
// Pause audio this.audioPlayer.pause();
// Stop the tick loop if (this.animationFrame) { cancelAnimationFrame(this.animationFrame); this.animationFrame = null; }
this.emit('pause'); }
/** * Seek to a specific time * * @param time - Time in seconds */ async seek(time: number): Promise<void> { const clampedTime = Math.max(0, Math.min(time, this.duration));
// Seek both video and audio this.videoWorker.seek(clampedTime); await this.audioPlayer.seek(clampedTime);
this.emit('seek', clampedTime); }
/** * Get the current playback time * * Queries the audio player's timeline, which is the source of truth. * * @returns Current time in seconds */ getCurrentTime(): number { return this.audioPlayer.getCurrentTime(); }
/** * Check if currently playing */ playing(): boolean { return this.isPlaying; }
private tick(): void { if (!this.isPlaying) return;
const now = performance.now(); const elapsed = now - this.lastFrameTime;
// Frame rate throttling: only update at TARGET_FPS // This prevents unnecessary rendering and saves CPU/battery if (elapsed < this.FRAME_INTERVAL) { this.animationFrame = requestAnimationFrame(() => this.tick()); return; }
this.lastFrameTime = now;
// Get current time from audio timeline (source of truth) const currentTime = this.audioPlayer.getCurrentTime();
// Check if we've reached the end if (currentTime >= this.duration - 0.1) { this.pause(); this.emit('ended'); return; }
// Emit tick event for UI updates // UI should listen to this rather than polling getCurrentTime() this.emit('tick', currentTime);
// Tell video worker to render at this time (passive) // Video worker doesn't track time itself - it just renders whatever we tell it this.videoWorker.render(currentTime); this.audioPlayer.checkForPreLoad();
// Schedule next tick this.animationFrame = requestAnimationFrame(() => this.tick()); }
/** * Update duration (if needed after initialization) */ setDuration(duration: number): void { this.duration = duration; }
/** * Clean up resources */ destroy(): void { if (this.animationFrame) { cancelAnimationFrame(this.animationFrame); this.animationFrame = null; } this.isPlaying = false; }}Player
Section titled “Player”Finally, we’ll include the player interface as described previously, which will instantiate all the components, and expose the pause/play/seek methods as well as event handlers via the on listener (which passes through to the Clock), so that it we can build a UI around it.
Player Class
import { VideoTrackData } from "./renderers/video/decoder";import EventEmitter from "../utils/EventEmitter";import { WorkerController } from '../utils/WorkerController';import { AudioTrackData, WebAudioPlayer } from "./renderers/audio/audio";import { VideoWorker } from "./renderers/video/video";import { Clock } from "./clock";import workerUrl from './file.ts?worker&url';// Note to Claude: Do not edit this file or make suggestions unless I specifically ask you to.
export interface WebCodecsPlayerParams { src: File; canvas: HTMLCanvasElement;}
export interface TrackData { duration: number, audio?: AudioTrackData video?: VideoTrackData}
export class WebCodecsPlayer { private canvas: HTMLCanvasElement | null = null; private params: WebCodecsPlayerParams; private file: File; duration: number = 0; private renderer: VideoWorker | null = null; private audioPlayer: WebAudioPlayer | null = null; private worker: WorkerController | null = null; private clock: Clock | null = null; private trackData: TrackData | null = null;
constructor(params: WebCodecsPlayerParams) { this.params = params; this.worker = new WorkerController(workerUrl); this.file = params.src; this.canvas = params.canvas; this.duration = 0; }
async play() { if (!this.clock) { throw new Error('Player not initialized. Call initialize() first.'); }
await this.clock.play(); }
async pause() { if (!this.clock) { throw new Error('Player not initialized. Call initialize() first.'); }
this.clock.pause(); }
async seek(time: number) { if (!this.clock) { throw new Error('Player not initialized. Call initialize() first.'); }
await this.clock.seek(time); }
getCurrentTime(): number { return this.clock?.getCurrentTime() || 0; }
terminate(){ // Clean up clock if (this.clock) { this.clock.destroy(); this.clock = null; }
// Clean up audio resources if (this.audioPlayer) { this.audioPlayer.pause(); // Any additional cleanup for audio... }
// Clean up renderer resources if (this.renderer) { if (this.renderer instanceof VideoWorker) { this.renderer.terminate(); } this.renderer = null; }
}
async initialize(): Promise<void> {
// Create file demuxer worker this.worker = new WorkerController(workerUrl);
// Create MessageChannel for file worker <-> video worker communication const videoChannel = new MessageChannel();
// Initialize file worker with video port await this.worker.sendMessage('init', { file: this.file, videoPort: videoChannel.port1 }, [videoChannel.port1]);
// Get track metadata from file worker const trackData = <TrackData> await this.worker.sendMessage('get-tracks', {}); console.log("Track data", trackData);
this.trackData = trackData; this.duration = trackData.duration;
// Initialize video worker with port to file worker this.renderer = new VideoWorker({ src: this.file, canvas: this.canvas!, fileWorkerPort: videoChannel.port2 });
await this.renderer.initialize();
// Send track metadata to video worker await this.renderer.setTrackData(trackData.video!, trackData.duration);
// Initialize audio player with file worker this.audioPlayer = new WebAudioPlayer({ worker: this.worker, audioConfig: trackData.audio!, duration: trackData.duration, file: this.file });
// Create clock to manage playback timing // The clock coordinates audio and video using the audio timeline as source of truth this.clock = new Clock(this.audioPlayer, this.renderer, this.duration);
// Forward clock events to external listeners
}
on(event, listener){ this.clock.on(event, listener) }
// Add more methods as needed}
export default WebCodecsPlayer;We’ll also expose getCurrentTime() and player.duration which we’ll need for the playback progress bar for a UI.
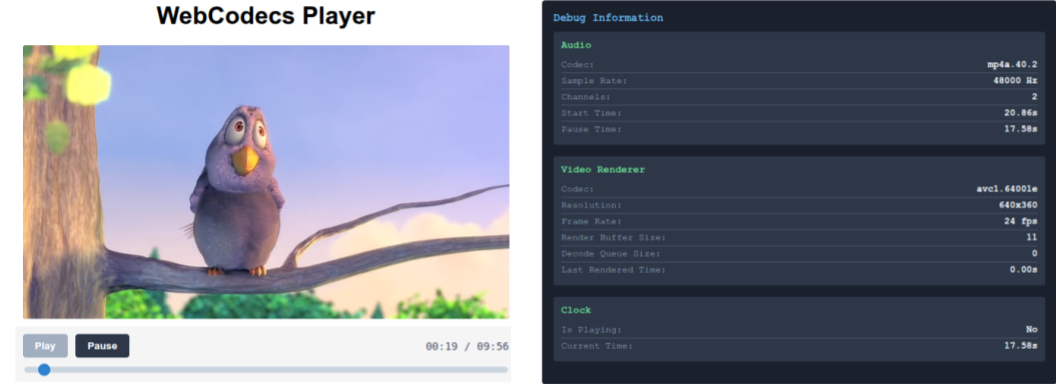
Now that we’ve built the player, we can go ahead and vibe-code a simple player interface, which will load a video file, or a demo video (Big Buck Bunny) and verify playback works.
You can see the full source code for the player here. You can see the source code for the demo here (html, js)
Now we’ve got a full working webcodecs based video player, and hopefully that provides enough structure to get started with video playback and adapt to your own use case.